
Announcing Illustrious Text‑Enhancer: Tag Booster & Mood Enhancer
Announcing Illustrious Text‑Enhancer: Tag Booster & Mood Enhancer
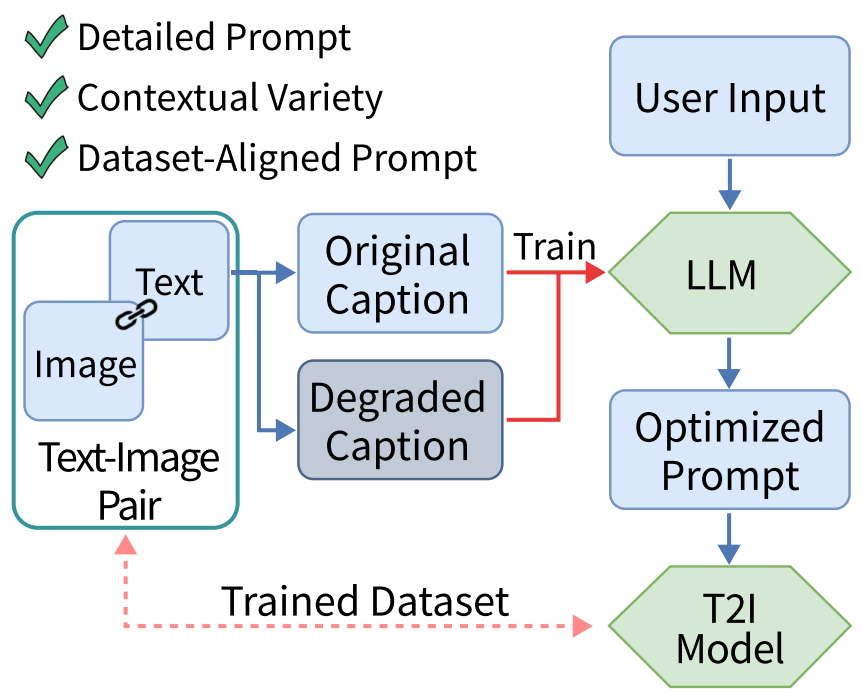
Illustrious users often ask: “How can I get better results without writing long prompts?” Today, we’re excited to answer that with Text‑Enhancer, a new system that dramatically enriches user prompts for our image generation platform.
Text‑Enhancer actually comprises two intelligent components working together:
- Tag Booster: A prompt enrichment tool built on our TIPO (Text-to-Image Prompt Optimization) framework. It expands short or sparse prompts (whether tags or plain text) by aligning them with the distributions seen in our model’s training data. The result is higher fidelity images and tighter prompt–image alignment.
- Mood Enhancer: A custom LLM-based pipeline that transforms minimal input into detailed, evocative image prompts. By leveraging a fixed system prompt and few-shot examples (with an advanced KV caching strategy), it can generate rich descriptions from sparse input at a fraction of the usual LLM cost and latency.
Together, Tag Booster and Mood Enhancer reduce the burden on creators to hand-craft lengthy prompts, while consistently yielding higher-quality, on-target generations. In this post, we’ll dive into how each component works, the technical innovations under the hood (from multi-task prompt models to LLM KV caching), and why this is a game-changer for Illustrious users.
From Sparse to Rich: How Tag Booster Enriches Prompts with TIPO
Creating a vivid image from a one-liner prompt is challenging – diffusion models like Illustrious XL were trained on datasets where prompts/captions have a certain richness and variety. Tag Booster bridges this gap by automatically expanding and refining your prompt to look more like those in the training distribution. It’s powered by our in-house TIPO framework, a lightweight multi-task language model purpose-built for prompt optimization.
What is TIPO?
TIPO stands for Text-to-Image Prompt Optimization – a novel approach that was co-developed by collaborating with a bright external researcher of multimodal model. Unlike brute-force prompt engineering or expensive large language model methods, TIPO uses a small, efficient model (hundreds of millions of parameters, rather than tens of billions) that was trained on prompt pairs. Essentially, it learned to take a simple prompt and output a richer one. Conceptually, it “samples refined prompts from a targeted sub-distribution” of the prompt space, which means it adds the kinds of details our diffusion model expects, while preserving the original intent. This yields significantly improved visual quality, coherence, and detail compared to using the raw prompt.
Joint-task Training (Tags ↔ Text)
A key innovation in Tag Booster’s TIPO model is that it’s joint-task – it can handle both tag lists and natural language and convert one to the other. During training, we gave TIPO two kinds of tasks: “tag-to-text” (e.g. take a list of terse tags and produce a full descriptive sentence) and “text-to-tag” (take a short sentence and predict important tags or keywords). By learning both directions, the model developed a flexible understanding of prompt semantics. In practice, this means Tag Booster can interpret your input format and enrich it appropriately:
- If you provide a list of tags or a few words, it will add high-impact visual tags that are statistically correlated with those concepts in the training data.
- If you provide a short sentence, it will expand it with additional descriptors or stylistic keywords, effectively translating free-form text into an enhanced tag-rich prompt.
For example, imagine you input just “an autumn forest”. This is short and might produce a generic result. Tag Booster might enrich this to something like:
- Input: autumn forest
- Tag Booster Output: autumn forest, golden sunlight, falling leaves, high detail, masterpiece, warm color palette

By adding details (“golden sunlight”, “falling leaves”) and style tags (“high detail, masterpiece”), the prompt now better matches what our model was trained on. These extra cues help the diffusion model focus on the intended scene and aesthetic. In internal tests, this approach yielded notable gains in image quality – our evaluators saw more vivid colors, fewer artifacts, and compositions that aligned more closely with the prompt intention. This echoes findings from the TIPO research, which reported “substantial improvements in aesthetic quality, significant reduction of visual artifacts, and enhanced alignment with target distributions” when using such prompt optimization.
More importantly, Tag Booster operates lightning-fast. Because TIPO is so lightweight, adding this step doesn’t slow down generation in any noticeable way – it’s a fraction of a second to enrich the prompt. And unlike heuristics that simply append a fixed set of “magic keywords”, Tag Booster is context-aware: it tailors the additions to your specific prompt content. The enriched prompt still feels like a natural extension of what you wanted, just with more detail and clarity. The end result is that users get higher-fidelity images with minimal extra effort, allowing even one-word prompts to shine as if they were carefully engineered.
Vivid Narratives with Less Effort: Mood Enhancer and LLM-Powered Expansion
While Tag Booster excels at adding relevant keywords and tags, we also wanted to help users who prefer natural language prompts or who have a certain mood or story in mind for their image. This is where Mood Enhancer comes into play. Mood Enhancer uses a custom Large Language Model (LLM) pipeline to transform a brief idea into a rich, atmospheric prompt. If Tag Booster is about precision and fidelity, Mood Enhancer is about creativity and storytelling infusing prompts with vivid scene descriptions, context, and emotional tone.
How it Works
We crafted a special system prompt for an LLM along with a set of few-shot examples so that it learns the style of an ideal Illustrious prompt. For instance, the system prompt might say something like “You are an artist assistant that turns short prompts into detailed visual descriptions. Include imaginative details and set the mood.” Then we provide a few examples of transformations (just like showing the model a before-and-after of prompts). With this fixed prompt template, when the user provides their input, the LLM will generate an elaborated prompt following those examples.
Consider a user input: “futuristic city at night”. That’s a cool concept but fairly high-level. Mood Enhancer would turn this into something like:
“A sprawlingfuturistic cityskyline at night, withneon-lit skyscrapersand flying vehicles weaving between the buildings. The streets below glow withholographic billboardsand reflected lights. A sense ofrainy ambiancewith puddles reflecting the vibrant neon signs adds acyberpunkmood.”
Notice how the sparse idea became a mini story: it preserved the core (“futuristic city at night”) but added concrete visual elements (neon lights, skyscrapers, holographic billboards) and mood (rainy, cyberpunk vibe). This kind of rich prompt can guide the diffusion model to generate an image that feels like a frame from a sci-fi film, rather than a generic city. The atmospheric flair and specific details are exactly what Mood Enhancer is designed to inject.

KV Caching: Supercharging LLM Efficiency Under the Hood
Using an LLM to expand prompts raises a concern: cost and speed. High-quality LLMs (with large parameter counts) can be slow or expensive to run, especially if you feed a long system prompt and examples each time. We tackled this challenge with a clever optimization: Key-Value cache reuse for the LLM’s prompts. This technique is inspired by recent advances in LLM deployment (even Anthropic’s Claude API introduced a similar prompt caching feature to cut costs by up to 90%).
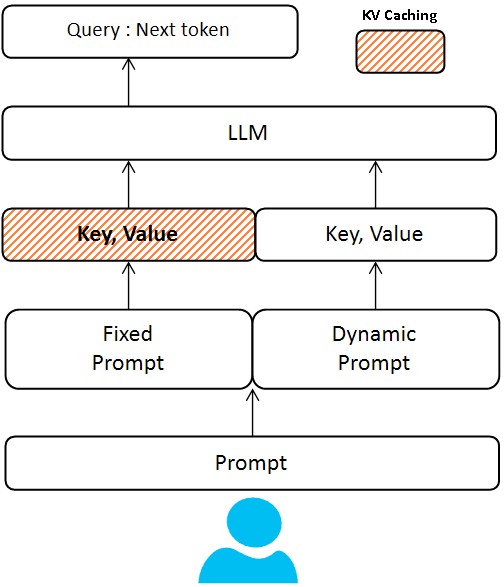
What is KV caching?
During autoregressive generation, LLMs build up internal Key and Value tensors (the “memory” of the self-attention mechanism) as they consume the prompt tokens. Normally, if you generate fresh each time, you pay the compute cost for all prompt tokens for each request. But if a large portion of the prompt is always the same (in our case, the system message and few-shot examples are fixed for Mood Enhancer), we can cache its KV state once and reuse it. In practice, we run the LLM through the static prompt portion one time (per session or server warm-up), and store the resulting key-value pairs from each transformer layer. Then for each new user input, we initialize the LLM’s state with this cached KV and start generation from the end of the prefix, as if the model had “already seen” the system prompt and examples.
This yields massive efficiency gains. The fixed prompt for Mood Enhancer can be quite lengthy (it might be, say, 500 tokens of instructions and examples to ensure high-quality output). With KV caching, those 500 tokens are processed just once; subsequent prompts only incur compute for the new user input (maybe 5–50 tokens) plus the output tokens. In our tests, this brought the LLM inference cost down to ~20% of the naïve cost per generation – effectively an 80% reduction in cost and a significant speedup, without any loss in output quality. These numbers line up with industry reports that prompt caching can reduce input costs by up to 90% in some scenarios.
Technical insight - making it work
Implementing KV caching in a robust way required navigating some LLM internals. Modern transformer models (including the one we use for Mood Enhancer) often employ rotary positional embeddings for tokens. This relative positioning scheme is great for handling long contexts, but we had to ensure that our caching mechanism preserves positional consistency. In simple terms, when we cache the prefix, the model has assigned certain positional phases to those tokens; when we later append the user’s tokens, we must continue the positional encoding seamlessly so that the model treats it as one continuous sequence. We addressed this by carefully managing the position indices during generation – essentially, the model is never “reset” between the prefix and user input, so there’s no chance for misalignment.
Another challenge was dealing with prefix-based limitations in standard generation pipelines. Off-the-shelf APIs or libraries typically assume you feed the entire prompt at once; they weren’t designed to let you inject a pre-computed prefix. To overcome this, we integrated low-level support that allows feeding the cached keys and values back into the model at generation time. Our solution is akin to what the latest LLM APIs now offer with prompt caching, but we custom-built it for our pipeline. We also took care to lock in the exact tokenization of the prefix so that nothing in the user input could inadvertently change how the prompt is parsed (a rare edge-case, but something we verified thoroughly). With these engineering fixes, Mood Enhancer can reuse its prompt context safely across many generations.
The result? Dramatically lower latency and cost for Mood Enhancer’s transformations, enabling us to offer this feature to users without noticeable delays. You get the benefit of a large-model prompt brainstorm for free, effectively, as the heavy lifting is amortized.
Text‑Enhancer in Action: Better Images with Minimal Effort
By combining Tag Booster and Mood Enhancer, Illustrious’s Text‑Enhancer system ensures that any user input, no matter how simple, can evolve into a powerful prompt for image generation. This is all done behind the scenes – you can toggle these enhancers on, enter a few words, and get back a beautifully detailed prompt and a stunning image.
Let’s walk through a hypothetical example to see the end-to-end effect:
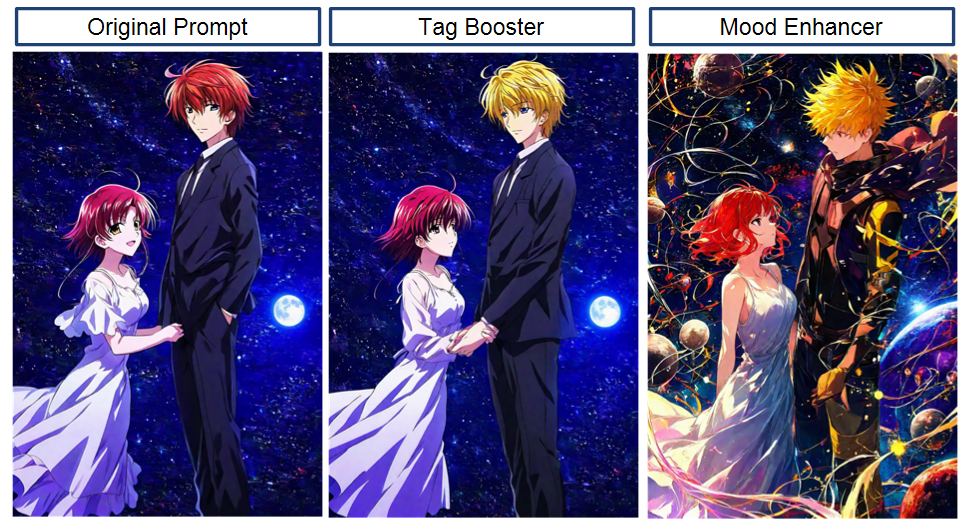
- User Input: a lone castle on a hill Just a simple description — evocative, but sparse. The user hasn’t specified style, lighting, or surrounding details.
- After Tag Booster: lone castle on a hill, medieval fortress, cloudy sky, twilight, high-resolution, epic scale Tag Booster recognized the theme and added key visual tags: the castle is identified as a medieval fortress, a likely setting (cloudy sky at twilight) is added for mood, and stylistic tags like “high-resolution, epic scale” align with our training data for dramatic scenery.
- After Mood Enhancer:“Alone medieval castlestands atop a misty hill under acloud-laden twilight sky*. The ancient stone fortress is illuminated by the last light of dusk, its silhouette towering withepic scaleover the darkening valley.Dramatic cloudsswirl above, and a faint mist clings to the ground, evoking amysterious, majestic atmosphere.”* Mood Enhancer wove the tags into a rich narrative. It preserved all the key elements (castle, hill, cloudy twilight) and enhanced them: we can nowfeel the atmosphereand see the scene in our mind’s eye.
Now imagine feeding the final enhanced prompt into Illustrious XL. The difference in the output is night and day. In fact, we tested this internally:
- Without Text‑Enhancer, the prompt “a lone castle on a hill” yielded a very generic castle image with a plain sky.
- With Text‑Enhancer, the generated image was far more dramatic and detailed – the castle had intricate architecture, the sky was filled with brooding clouds lit by the sunset, and the overall composition matched that “majestic atmosphere” we were aiming for.
Conclusion
The Illustrious Text‑Enhancer (Tag Booster + Mood Enhancer) represents a significant leap forward in bridging natural human input and the optimal prompts needed for high‑quality image generation. By leveraging advanced NLP techniques from a specialized prompt optimizing model (TIPO) to a cost‑efficient LLM pipeline our system handles the heavy lifting of prompt engineering in real‑time. This means artists and creators can focus on their creative vision, without getting bogged down in figuring out the perfect combination of keywords or descriptors.
From a technical perspective, we’re proud of how these components complement each other. Tag Booster ensures the prompt covers all the critical visual cues and aligns with our diffusion model’s training data, improving fidelity. Mood Enhancer takes it further by infusing the prompt with imaginative detail and atmosphere, yielding outputs that tell a story. And thanks to optimizations like KV caching, we achieve these gains without introducing lag or exorbitant compute costs a win-win for users and the platform.
We believe this will empower both newcomers and power users of Illustrious. Novices can get great results with minimal input, and experts can save time when fleshing out their ideas. It’s another step toward making AI image generation more intuitive and aligned with your creative intent.
The Text‑Enhancer features are live now in Illustrious : give them a spin! Start with a simple idea, enable Tag Booster and Mood Enhancer, and watch as your humble prompt transforms into a masterpiece‑worthy description. You’ll be greeted with an image that not only reflects what you imagined, but does so with a level of detail and quality that might just surprise you.
Happy prompting, and as always, let us know your feedback. We’re excited to see what you create with Tag Booster and Mood Enhancer supercharging your imaginations!